Node.js has become a major part of the modern web. You can quickly develop and deploy web apps with it.
Node.js (or Node) is supported by npm (Node.js Package Manager). It’s an open-source library of Node.js packages. So you can use one in your application without needing to rewrite the entire thing all on your own.
Node and npm are often installed and used together.
If you want to install Node.js on Ubuntu Linux, you’re in luck. Node.js is available in the Ubuntu repository and you can easily install it with a few commands.
However, it may not always be the latest version. To get the latest Node version, you can add the official Node repository.
There is also Node Version Manager for advanced users.
To summarize:
- Using Ubuntu’s official repository: Easy to install using apt but might have an older version.
- Using NodeSource repository: Slightly more complicated but you can choose to install from the currently available Node versions.
- Using Node Version Manager (NVM): This is a per-user installation of Node.js, where you can switch between multiple versions.
This tutorial will discuss all three methods of installing Node and npm.
Method 1: Install Node.js and npm on Ubuntu using the official repository
As I said earlier, Node.js is available on Ubuntu. So all you need to do is to open a terminal and use the following command:
sudo apt install nodejs npmI recommend installing npm as well because you’re going to need it anyway. Both Node.js and npm are quite small.
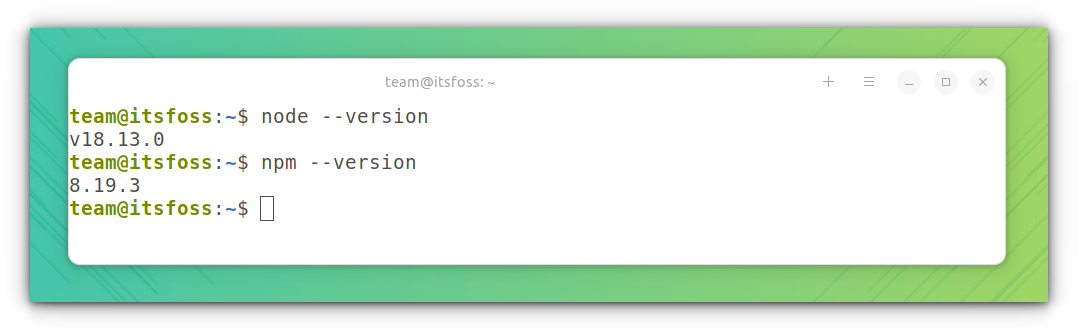
Once installed, you verify it by checking the installed version of Node.js and npm with this command:
node --version
npm --versionThe output should be like this:
ln -s /usr/bin/nodejs /usr/bin/nodeFor working on Node.js, you can use any good code editor for Linux or an IDE.
I’m not going to show you how to get started with Node.js because that’s not the purpose of this quick tutorial.
Remove Node.js
If you want to remove Node.js and npm, you can use the command below:
sudo apt remove nodejs npmNow that you learned the easiest method, let's see another way of getting Node straight from its developers.
Method 2: Install Node.js and npm using the NodeSource repository
You can install Node.js and npm directly from the NodeSource repository. Node.js provides an easy-to-use bash script for this purpose.
Let’s say you want to install Node.js version 18. First, install Curl on Ubuntu:
sudo apt install curlNow you can use the following command:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | sudo -E bash -If you want to install Node.js version 19, you can replace setup_18.x with setup_19.x.
The above command will download and start running the installation script. The script will add a new repository in the source list directory (/etc/apt/sources.list.d). It will also add the GPG key of the new repository automatically.
With this new repository added to the sources list, you can install Node.js using the apt command. The added advantage is that the installed Node.js version can be updated easily like a regular package using the sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade command.
To install the Node.js package, use the following command. Npm is also installed with this package automatically.
sudo apt install nodejsInstall an LTS version of Node.js
NodeSource repository provides a method to install the latest LTS (long term support) release, which at the time of updating this article is v18.x. To install this, use the following command to add the repository:
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_lts.x | sudo -E bash -Now, install Node.js LTS version by:
sudo apt install nodejsThis will install both nodejs and npm packages.
Remove Node.js
To completely remove Node.js installed from the NodeSource repository, first, you need to uninstall the packages installed:
sudo apt purge nodejsNow, remove the entry in the Sources List:
sudo rm -r /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.listMethod 3: Install Node.js and npm using the Node Version Manager
Node version manager is an easy-to-use per-user installation of Node.js and npm. With the help of NVM, you can install and switch between different versions of Node.js.
In order to install it, use the following command:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.3/install.sh | bashThis will clone the NVM repository in ~/.nvm and tries to add all the required entries to your shell configuration files.
Once set up, restart your current shell. To check the status of NVM, use:
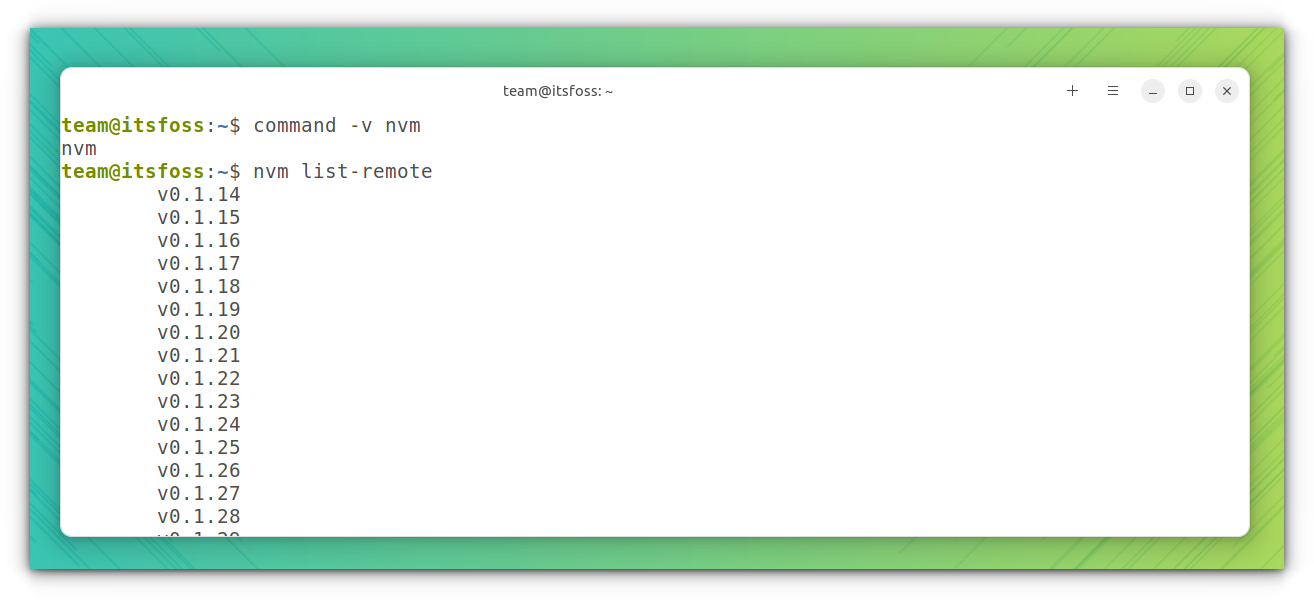
command -v nvmIt would output the following if the setup is a success:
[email protected]:~$ command -v nvm
nvmNow you can run the following command to list all available versions of Node.js:
nvm list-remoteYou will get a long list of versions, as shown in the screenshot below:
Once you confirmed the Node.js version, use the following command to install it:
nvm install <nodejs-version-number>The above command will install Nod version 18 and a compatible NPM version. Similarly, you can give any version number to install that particular version of Node.js and a corresponding NPM.
In order to switch to an installed Node.js version, use:
nvm use <any-of-your-installed-version-number>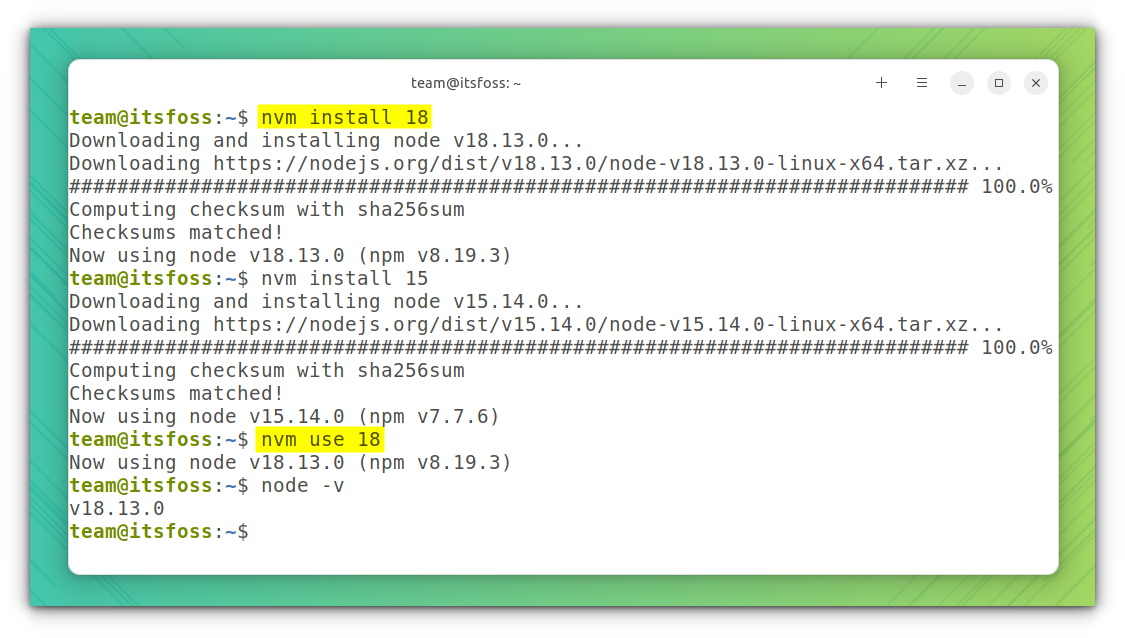
Remove NVM versions
To uninstall a version of Node.js installed with nvm, use:
nvm uninstall <version>nvm deactivate before removing it, if that version is currently in use.And to remove the NVM completely, use the following command:
rm -rf "$NVM_DIR"Now, remove the following lines from your ~/.bashrc:
export NVM_DIR="$HOME/.nvm"
[ -s "$NVM_DIR/nvm.sh" ] && \. "$NVM_DIR/nvm.sh" # This loads nvm
[[ -r $NVM_DIR/bash_completion ]] && \. $NVM_DIR/bash_completion
Wrapping Up
I focused on the installation part here but I won't leave you just at that. Here's a cheat sheet that lists basic node and npm commands for your quick reference.
There are other methods to install Node.js in Ubuntu and other Linux distributions, like installing from the source, using pre-built binaries, etc. Please refer to the Node.js official documentation for more details.
That’s all you need to do to install Node.js on Ubuntu. I hope you found this quick tip helpful. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to leave a comment below.
After that, if you love Node.js, you should check out NodeOS, a Linux distribution for Node.js users.

